Herrmann Develops Software for H1N1 Vaccinations
July 21, 2009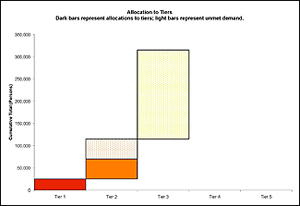
Should state or local jurisdictions receive a limited number of vaccinations (doses of vaccine), their public health officials will have to determine how many persons from which target groups can be treated.
A research team led by Associate Professor Jeffrey Herrmann (ME/ISR) has developed and released Vaccine Allocation Model v.1.4, a Microsoft Excel workbook that helps to answer this question.
Vaccine Allocation Model can help public health officials determine if a given number of doses of a vaccine will be sufficient to vaccinate (treat) everyone who wishes to be treated. If the number of doses is insufficient, the Vaccine Allocation Model will determine how many persons in different target groups can receive treatment.
The Vaccine Allocation Model can be used either in the advance planning stages of a vaccination campaign or for support during a campaign. It is based on information published in Guidance on Allocating and Targeting Pandemic Influenza Vaccine, a joint publication of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and the U.S. Department of Homeland Security.
Based on the pandemic severity, the number of vaccinations available, and the population of each target group in a state or jurisdiction, the model determines how many persons in each target group can be treated in a way that follows the federal government priorities.
Herrmann's team worked closely on the model with their partners at the Montgomery County (Md.) Advanced Practice Center for Public Health Emergency Preparedness and Response. Rachel Abbey of their staff, along with Hiro Toiya at the Hawaii State Department of Health, provided valuable feedback on draft versions of the model.
The model can be downloaded free of charge at the Vaccine Allocation Model website.
You can read more about the model at Herrmann's Public Health Preparedness Modeling blog.